记录了模拟退火的原理和matlab第三方工具箱satools的使用。
算法原理
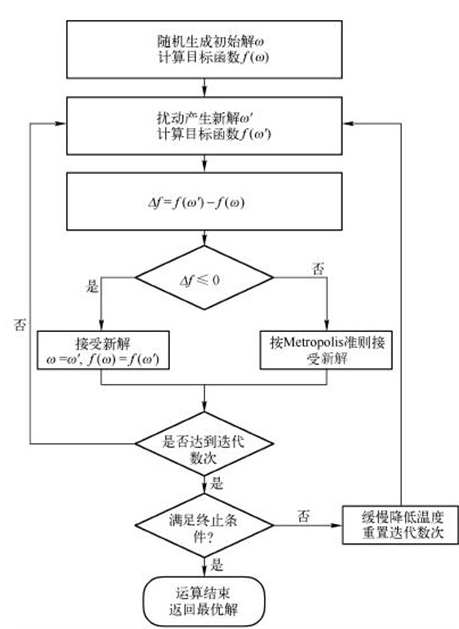
SATOOLS使用
模拟退火主函数anneal
调用格式:
1 | function [W,Ew,Wbsf,Ebsf,Tt,Et,Etarget,ert,Kt,Ebsft,Eh,M,rho,Ebin] = anneal( ... |
参数说明
输入参数
verbose:flag变量,为1时打印状态变量newstate:用户自定义函数,产生初始解X:问题的domain(解空间?),常量cost:用户自定义函数,最优化的目标函数moveclass:用户自定义函数,用来产生新解walkers:正整数acceptrule:用户自定义函数,接受规则,工具箱也提供了几个,经常用metropolis准则q:acceptrule所需要的参数schedule:温度更新函数,可自定义P:schedule所需参数equilibrate:(平衡)可传入函数句柄或其他。当传入函数时,表示温度是否改变的判断函数C:equilibrate所需参数maxsteps:同一温度下的迭代最大次数Tinit:初始化函数,可自定义可使用工具箱提供函数。r:Tinit所需参数Tfinal:终止温度,可以是自定义函数,工具箱也提供,或者是数(-INF ok)f:参数maxtemps:最大温度迭代次数v:温度变化的快慢$[0,1]$bins:e:
输出参数
W:每个walker的最终状态Ew:W对应的最终能量Wbsf:每个walker的best so far状态Ebsf:每个walker的best so far能量Tt(i):每次温度步的温度记录Et(i):Tt(i)对应的平均能量Etarget(i):Tt(i)对应的目标平均能量,根据v计算ert(i):kt(i):Tt(i)对应的热平衡步数Ebsft(i):Tt(i)对应的best so far能量Eh:能量和温度的历史记录i = 1,1 + (steps*walkers)Eh(i,1):温度步的下标tEh(i,2):t对应的温度TEh(i,3):在温度T时的达到热平衡步数的编号jEh(i,4):walker的编号kEh(i,5):在T温度下,第j步,walker k对应的能量Eh(i,6):在T温度下,第j步,energy E' attempted from E
M:rho:Ebin:
自定义函数编写
newstate产生初始解,1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13function W = PROBLEMNAME_new(X)
% W = PROBLEMNAME_new(X)
% See http://www.frostconcepts.com/software for information on SA Tools.
%
% W = PROBLEMNAME_new(X) ;
%
% X = behaviorally constant application data
%
% W = specific data about current state
%
% Instantiates a new state.
%
W = [] ; % a typical application will put state specific data herecost最优化目标1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10function Ew = PROBLEMNAME_cost(X,W)
% Ew = PROBLEMNAME_cost(X,W)
%
% X = behaviorally constant application data
%
% W = specific data about current state
%
% Ew = energy corresponding to W
%
Ew = rand ; % a typical application will use information from W and X to compute Ew.moveclass产生新解1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9function W = PROBLEMNAME_perturb(X,W,Ea,T)
% W = PROBLEMNAME_perturb(X,W,Ea,T)
%
% X = behaviorally constant application data
%
% W = (on input) current state, (on output) next state.
%
% Ea = current average energy
% T = current temperature产生解空间
1
2
3
4
5
6function X = PROBLEMNAME_init()
% X = PROBLEMNAME_init()
%
% X = behaviorally constant application data
%
X = [] ; % a typical application will put problem domain data here